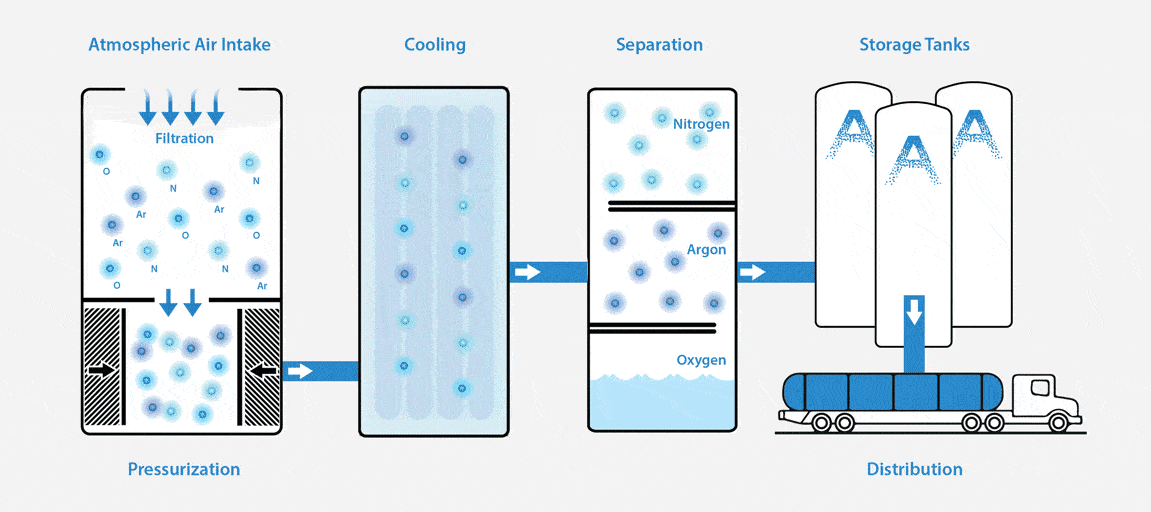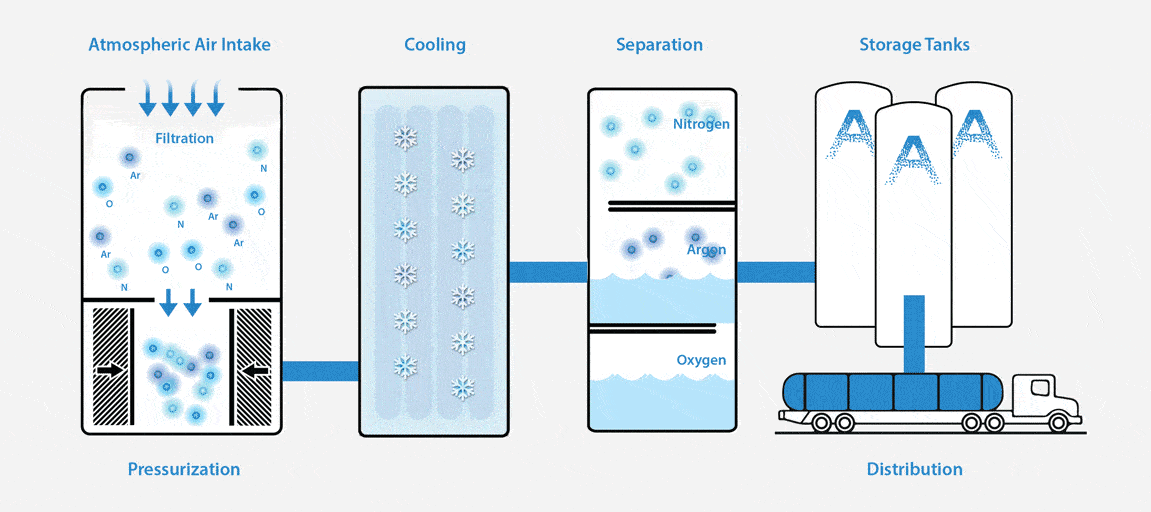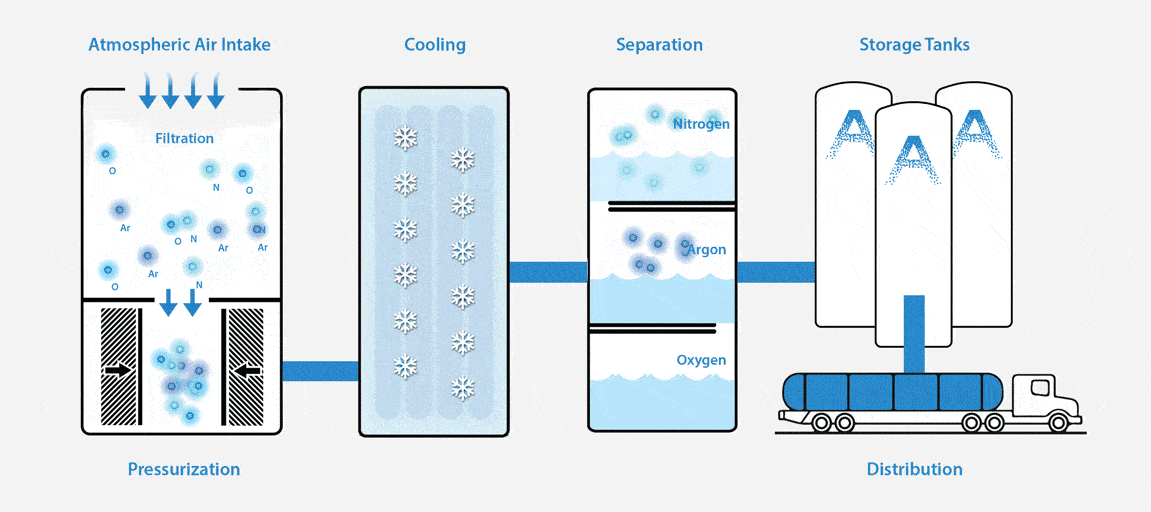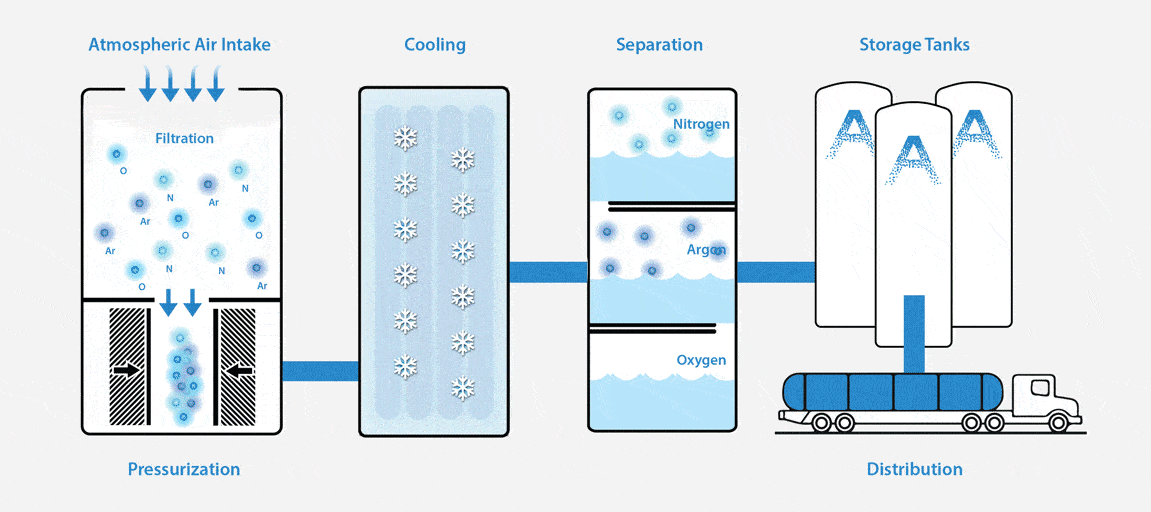
What is an ASU and How Does it Work?
An Air Separation Unit (ASU), or otherwise known as an air separation plant, separates atmospheric air into its primary components — typically nitrogen, oxygen, and argon.
To put it simply, an ASU works like this: